Hepatitis basically means an inflammation of the liver. The etiology is quite broad and can be narrowed based on history. Hepatitis can be broadly classified into acute and chronic forms, each with their own clinical significance. It is important to understand the clinical symptoms, initial investigations, and when it is important to refer a patient for further evaluation.
History[]
- Symptom screen
- asymptomatic, fever, N/V, Jaundice, abdominal pain/distention, dark urine, pale/clay colored stool, anorexia, pruritus, other extra-stigmata of liver disease
- Exposure history
- Substance use: Alcohol, IVDU
- Drug use: OTC medications (Tylenol), prescription medications
- Sexual history
- Travel history - fecal/oral transmission
- History of blood transfusion
- Recent infectious symptoms
- Immunization history (Hep A/B)
- Past medical history
- Autoimmune d/o
- Right sided heart failure
- Metabolic syndrome
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Hemochromatosis, wilson's, alpha-1- antitrypsin
- Vascular disease - ischemia
- Family history
- Pregnancy
Physical Examination[]
- ABCs + Vitals + GCS
- General: temporal/proximal muscle wasting, jaundice, icterus, confusion (hepatic encephalopathy)
- Abdominal Examination
- + ascites (fluid wave, shifting dullness, bulging flanks)
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- General abdominal exam - r/o tenderness
- Extrastigmata of liver disease:
- asterixis, spider nevi, palmar erythema, gynecomastia, caput medusa, dupuytren's contractures, parotid enlargement, testicular atrophy, umbilical hernia
Investigations[]
Liver enzymes[]
- ALT - alanine aminotransferase
- AST - aspartate aminotransferase (can be elevated in muscle d/o)
- ALP - alkaline phosphatase (can be elevated in bone d/o)
- GGT - gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Liver function[]
- Albumin
- INR/PTT
- Glucose
- Bilirubin
- Indirect bilirubin elevation (prehepatic)
- overproduction (hemolysis, ineffective erythropoiesis)
- Impaired uptake/conjugation (drugs, genetic d/o)
- Direct bilirubin elevation
- Hepatic etiology
- Cholestatic etiology
- Indirect bilirubin elevation (prehepatic)
Hepatocellular[]
- Elevated AST and ALT +/- elevation in bilirubin
- Serology for Hep A/B/C
- +/- acetaminophen level
- +/- other drug levels,
- +/- Hemochromatosis w/u: ferritin, transferrin level, genetic testing
- +/- Wilson's w/u: ceruloplasmin level, liver biopsy (gold standard)
- +/- Autoimmune w/u: ANA, anti-smooth muscle antibody, serum immunoglobulins, SPEP, liver kidney microsomal type 1 (LKM-1)
- +/- Alpha-antitrypsin w/u: serum alpha-antitrypsin levels
- +/- Serology CMV, EBV, HSV, VZV
- +/- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: lipid profile
- +/- Ischemic/shock liver: lactate, clinical picture
Cholestatic (obstructive pattern)[]
- Elevated ALP, GGT +/- Bilirubin
- Obtain ultrasound or CT to r/o obstruction
- +/- MRCP/ ERCP
- Etiology: gallstones, strictures, tumors,
Hepatitis A[]
- Transmission: Fecal-oral route
- Incubation period: 15-50days
- Clinical:
- Pre-icteric: abrupt onset of fever, N/V, abdominal pain
- Icteric: elevated conjugated bili, jaundice, dark urine, pale stools
- Fulminant illness <1%
- Often lasts < 2 months. Can have prolonged course up to 6 months. Does not become chronic
- Virus killed by heating > 85 degrees C
- Investigations: Hep A IgM
- Prevention: vaccination, hand-washing, avoid contaminated water
- Treatment
- acute: supportive management, avoid hepatotoxic medications
- fulminant: liver transplant
- Close contacts/post exposure prophylaxis:
- Immune globulin available if not immunized. Must be administered within 2 weeks after exposure for maximum protection
Hepatitis B[]
- Transmission: contact with infectious blood or bodily fluids
- Able to survive outside the body for 7 days
- Incubation period: 90 days
- Classification:
- Acute Hepatitis B: symptoms weeks-6months. Spectrum of disease: Asymptomatic to fulminant liver failure
- Chronic Hepatitis B (higher rate for children, adults approximately 5% become chronic)
- Perinatal Hepatitis B
- Investigations:
- NOTE: HBsAg with be detected in blood 4 weeks after exposure
- Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg): indicates patient is infectious
- Hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs): recovery or immunity (previous vaccination)
- Hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc): previous or ongoing infection
- IgM anti-HbC (core): recent infection < 6 months
- Hepatitis B e antigen (HbeAg): indicates viral replication. Higher infectivity.
- Hepatitis B e antibody: predictor of long term clearance, used to monitor treatment

- Close contact/post-exposure prophylaxis:
- Hep B vaccination +/- Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin (within 24 hours)
- Vaccination:
- Contraindication: allergy
- Can be given to pregnant and immunocompromised individuals
- Offers 20 years of immunity
- See IMMUNIZATION SECTION
- Treatment:
- Acute: supportive
- Chronic: refer for further evaluation (hepatology), monitor for complications of chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. May be candidate for anti-virals
- **Test for other infections - HIV and Hep C
- Safe practices counselling: safe sex, safe IV use
Hepatitis C[]
- Transmission: exposure to infectious blood
- Risk in blood transfusion: 1: 2 million units
- Risk in needlestick: 1.8 %
- Pathophysiology: multiple genotypes of hepatitis C. Therefore able to be re-infected with an alternate strain
- Risk of becoming chronic 75-85%, risk of cirrhosis 5-20%, risk of HCC 1-5%
- Vaccination: none
- Investigations: anti-HCV (if non-reactive---> no further investigation. Positive in 4-10 weeks).
- If recent exposure test HCV RNA (positive in 2-3 weeks)
- HCV PCR and genotype
- If recent exposure test HCV RNA (positive in 2-3 weeks)
- Treatment:
- **Test for other infections - HIV and Hep C
- Safe practices counselling: safe sex, safe IV use, blood donation
- Vaccinate against Hep A/B, consider other immunizations
- Avoid ETOH and other hepatotoxic medications
- Refer for further assessment - hepatology/internal medicine
- Treatment options:
- ribaviron+ pegalated interferon for HC genotype 1 x 24-48 weeks
- New: sofosbuvir (sovaldi- nucleotide analogue inhibitor) and simeprevir (olysio - protease inhibitor)
- Other complications (rare): diabetes mellitus, glomerulonephritis, non-Hodgkins lymphoma, essential mixed cryoglobulinemia
Cirrhosis[]
- Etiology of cirrhosis
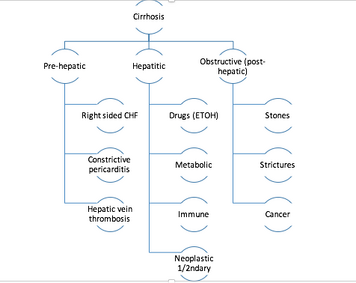
- Metabolic: NASH, Wilson's, Hemochromatosis, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
- Immune: autoimmune, PBC, sclerosing cholangitis
- Ensure vaccination status (including Hep A/B)
- Avoid hepatotoxic substances
- Monitor liver enzymes and liver function routine
- Use MELD score: disease severity scoring system for 3 month mortality
- Monitor for hepatocellular carcinoma (ultrasound +/- AFP) q 6 months
- Monitor for complications:
- Esophageal varices
- Ascites +/- spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Hepatorenal syndrome
- Portal hypertension
Resources[]
http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hav/havfaq.htm